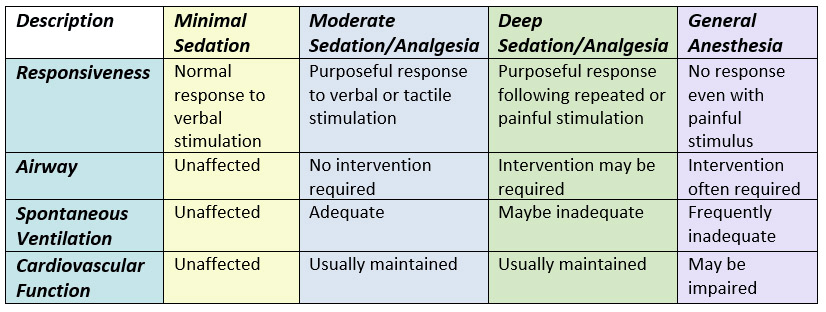
Levels of Sedation
Equipment
- Cardiac monitor
- BVM
- Oral / Nasal airways; supplemental oxygen
- Capnography – etCO2 >50 mmHg, or an increase in etCO2 >10 mmHg indicates hypoventilation
- Intubation equipment
- Defibrillator
- IVF
Pre-procedural Analgesics
- Fentanyl 1-2 mcg/kg
Wait 2-3 minutes for peak effect of the opioid to minimize risk of respiratory depression and apnea
Procedural Sedation Agents
Propofol
- Dosing: 1 mg/kg; repeat dosing 0.25-0.5 mg/kg (Based on ideal body weight)
- Onset: 10-50s
- Duration: <10 min
- Advantages: Rapid onset, short duration of action, good for orthopedic reductions (Provides moderate to deep sedation)
- Disadvantages: No analgesic effect, respiratory depression, hypotension
Ketamine
- Dosing: 1-1.5 mg/kg (administer slowly); pediatrics usually requires higher 1.5 mg/kg dosing; repeat dosing 0.5-1 mg/kg
- Onset: 30-40s
- Duration: 5-10 min
- Advantages: Provides sedation, analgesia, and cardiorespiratory stability; useful for longer procedures; useful for patients at risk for bronchospasms
- Disadvantages: Emergence reaction (can pretreat with Zofran and versed), avoid in psychotic or schizophrenic patients
Etomidate
- Dosing: 0.1 mg/kg; repeat dosing; repeat dosing 0.05 mg/kg
- Onset: 10-20s
- Duration: 2-3 min for 0.15 mg/kg dose
- Advantages: Hemodynamically neutral agent; Minimal cardiovascular and respiratory depression; ideal for short procedures, cardioversion
- Disadvantages: Myoclonus, adrenal suppression in the critically ill
Ketofol
- Dosing: 0.5mg/kg Ketamine + 0.5mg/kg propofol
- Onset: <1 min
- Duration: <10 min
- Advantages: Ketamine adds analgesia without opioids and blunts propofol induced hypotension
- Disadvantages: Higher ketamine:propofol ratios lead to longer recovery
Midazolam
- Dosing: 1 – 2.5 mg OR 0.1 mg/kg (0.05 mg/kg in the elderly)
- Onset: 3-5 minutes
- Duration: 30-80 minutes
- Advantages: Use during longer procedures requiring deep sedation
- Disadvantages: Provides no analgesia, and can cause cardiovascular and respiratory depression when combined with opioids
Fentanyl
- Dosing: 0.5-1.5 mcg/kg
- Onset: 3-5 min
- Duration: 30-60 minutes
- Advantages: Monotherapy can be used for minimal sedation; provides analgesia
- Disadvantages: Respiratory depression
Dexmedetomidate (Precedex)
- Dosing: 1 mcg/kg over 10 min then maintain infusion of 0.6 mcg/kg/hr
- Onset: 4-5 min
- Duration: 45-90 min
- Advantages: Useful for cooperation in a patient experiencing respiratory depression (Sedation without respiratory depression)
- Disadvantages: Hypotension; blunts sympathetic response
Dosing Considerations
Obesity
- Etomidate, ketamine, fentanyl and propfol are highly lipophilic and protein bound and should be dosed according to ideal body weight
- Benzodiazepines i.e. Midazolam have a volume of distribution that correlates with excess fat tissue and should be dosed according to total body weight
Pregancy
- Consider using propofol or fentanyl, but consult OB if able regarding the best PSA agent
Leave a comment