Determine if the patient is DNR. If no, you can proceed.
Priorities
- Focus on chest compressions. Think CAB (Circulation, Airway, Breathing), but prioritize the airway if you think that this was a respiratory arrest due to inadequate oxygenation (e.g. bad tube)
- A LMA is an efficient and appropriate airway while chest compressions are being performed
- Get the pads on. You’re checking every 2 minutes for a shockable rhythm.
- Get a POC glucose (if this isn’t already a priority). Everyone already knows to get access and draw labs.
- Throw in a IO if no one can get access
- Determine if there are any reversible causes
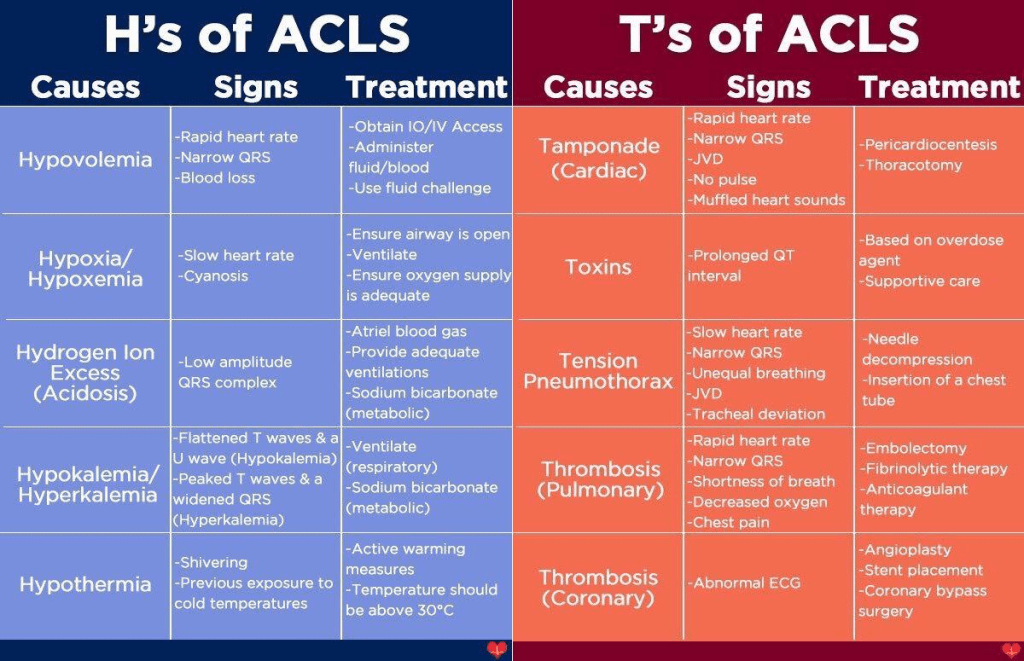
The Role of Ultrasound in Identifying Reversible Causes for Cardiac Arrest
- Cardiac – no more guessing for cardiac activity or if there is a pulse; r/o tamponade, massive PE, dissection
- Lung – r/o tension pneumothorax
- FAST – determine if the patient is exsanguinating into their abdomen
Medications
- Epinephrine 1mg every 3-5 minutes
- Amiodarone 300mg bolus, and a subsequent 150mg dose for ventricular dysrhythmias
- Do not give to patients with atrial fibrillation with an accessory pathway, polymorphic VTach
- Lidocaine 1-1.5mg/kg
- Sodium channel blocker that suppresses ventricular ectopy
- Bicarbonate – only indicated for TCA overdose and hyperkalemia
- Do not use for acidemia
- TPA
- Only indicated if you think the patient arrested because of a massive PE
- Magnesium
- Indicated for polymorphic VTach, or hx of prolonged QT
- Calcium
- Indicated in patients with renal failure
ACLS Algorithm

Leave a comment